Table of Contents
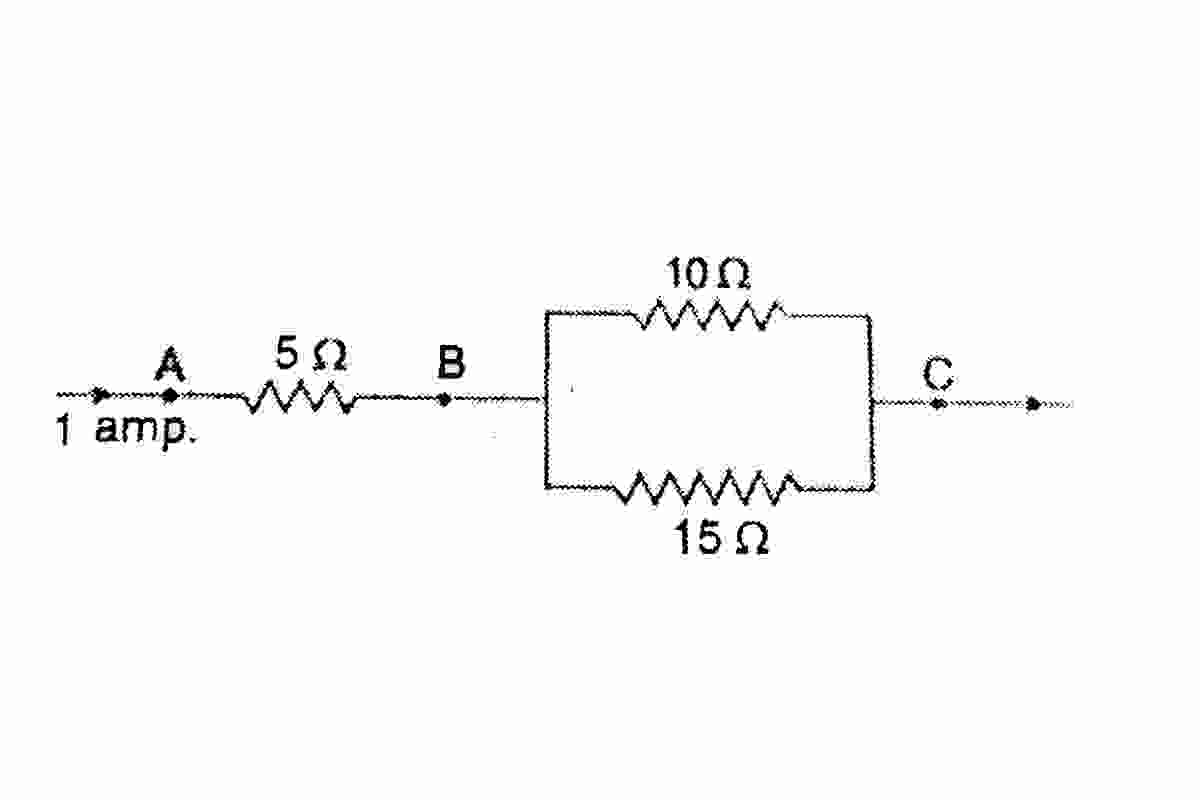
Three Resistors are Connected as shown in the Diagram
The Resistor is a two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. Three Resistors are Connected as shown in the Diagram. In electronic circuits, resistors use as to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, divide voltage, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses.
Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. High-power resistances that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat, maybe use as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators.
Variable Resistors
Variable resistors can be use to adjust circuit elements (such as volume control or a lamp dimmer), or as sensing devices for heat, light, moisture, force, or chemical action.
The electrical purpose of a resistor is specified by its resistance: common commercial resistors are factory-made over a range of more than nine orders of greatness. The nominal value of the confrontation falls within the manufacturing tolerance, indicated on the component.
Resistors are common rudiments of electrical networks and electronic circuits and are ubiquitous in electronic equipment. Resistors are also implemente within integrate circuits. Practical resistors as discrete mechanisms can compose of various compounds and forms.
Power Dissipation
Resistors require to dissipate substantial amounts of power, particularly use power supplies, power conversion circuits, and power amplifiers, are generally referre to as power resistors; this designation is loosely applie to resistors with a power rating of 1 watt or greater. Power resistors are physically larger and may not use the preferred values, colour codes, and external packages described below.
Excessive power debauchery may raise the temperature of the resistor to the point where it can burn the circuit board or adjacent components, or even cause a fire. if the average power dissolute by a resistor is more than its power rating, damage to the resistor may occur, permanent altering its resistance; this is distinct from the reversible change in resistance due to its temperature coefficient when it warms. There are fireproof resistors that fail (open circuit) before they overheat dangerously.
Nonideal Properties
Practical devices have a series inductance and a small parallel capacitance; these specifications can be important in high-frequency requests. In a low-noise loudspeaker or pre-amp, the noise features of a resistor may be an issue.
The temperature coefficient of the confrontation may also be of anxiety in some exact applications.
The wanted inductor, excess noise, and temperature coefficient are mainly dependent on the technology use in the industrial resistors. Moreover, Three Resistors are Connected as shown in the Diagram. They are not usually specified individually for a specific family of resistors manufacture using a particular technology.
A family of separate resistors is also characteriz according to its form factor, that is, the size of the device and the position of its leads (or terminals) which is relevant in the practical manufacturing of circuits using them.
Resistors with higher power scores are physically larger and may need heat sinks. In a high-voltage circuit, care must sometimes paid to the rate maximum working voltage of the resistor.